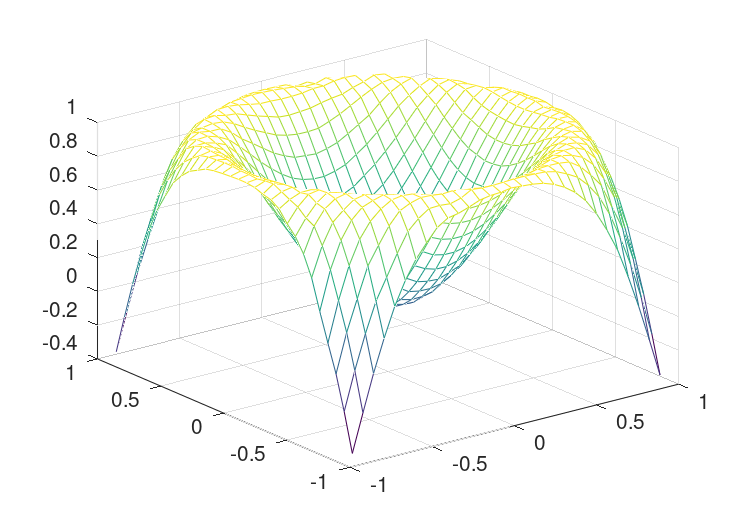
Figure 30.6: Interpolation from a scattered data to a regular grid
Next: Vector Rotation Matrices, Previous: Convex Hull, Up: Geometry [Contents][Index]
An important use of the Delaunay tessellation is that it can be used to
interpolate from scattered data to an arbitrary set of points. To do
this the N-simplex of the known set of points is calculated with
delaunay or delaunayn. Then the simplices in to which the
desired points are found are identified. Finally the vertices of the simplices
are used to interpolate to the desired points. The functions that perform this
interpolation are griddata, griddata3 and griddatan.
Generate a regular mesh from irregular data using interpolation.
The function is defined by z = f (x, y). Inputs
x, y, z are vectors of the same length or
x, y are vectors and z is matrix.
The interpolation points are all (xi, yi). If xi,
yi are vectors then they are made into a 2-D mesh.
The interpolation method can be "nearest", "cubic" or
"linear". If method is omitted it defaults to "linear".
Generate a regular mesh from irregular data using interpolation.
The function is defined by v = f (x, y, z).
The interpolation points are specified by xi, yi, zi.
The interpolation method can be "nearest" or "linear".
If method is omitted it defaults to "linear".
The optional argument options is passed directly to Qhull when
computing the Delaunay triangulation used for interpolation. See
delaunayn for information on the defaults and how to pass different
values.
Generate a regular mesh from irregular data using interpolation.
The function is defined by y = f (x).
The interpolation points are all xi.
The interpolation method can be "nearest" or "linear".
If method is omitted it defaults to "linear".
The optional argument options is passed directly to Qhull when
computing the Delaunay triangulation used for interpolation. See
delaunayn for information on the defaults and how to pass different
values.
An example of the use of the griddata function is
rand ("state", 1);
x = 2*rand (1000,1) - 1;
y = 2*rand (size (x)) - 1;
z = sin (2*(x.^2+y.^2));
[xx,yy] = meshgrid (linspace (-1,1,32));
zz = griddata (x, y, z, xx, yy);
mesh (xx, yy, zz);
that interpolates from a random scattering of points, to a uniform grid. The output of the above can be seen in Figure 30.6.

Figure 30.6: Interpolation from a scattered data to a regular grid
Next: Vector Rotation Matrices, Previous: Convex Hull, Up: Geometry [Contents][Index]